Animal and human bites
OVERVIEW
What are the characteristics of animal and human bites?
- Dog bites: Male dogs and certain breeds, such as German Shepherds and Pit Bulls, are more likely to bite, especially children. This may be because young children play around dogs, and their head height is similar to the mouth level of large dogs, making head and neck bites more common.
- Cat bites: Cats typically cause wounds with their teeth or claws, and 89% of cat bites occur when the cat is provoked.
- Human bites: Human bites can be divided into two types: one where teeth break the skin, and the other where skin impacts teeth, causing damage to the skin and underlying structures. This often occurs on the skin of hand joints, such as during fights.
Are animal and human bites common?
Animal bites are common worldwide. In low- and middle-income countries, animal bites are a significant route of rabies transmission. The vast majority of mammalian bites are dog bites (60%–90%), followed by cat bites (5%–20%), human bites (2%–3%), and bites from other animals.
Which department should you visit for animal or human bites?
Emergency department.
SYMPTOMS
What are the clinical manifestations of animal and human bites?
- Dog bites: Dog bites can range from minor wounds like scratches and abrasions to severe injuries such as deep open lacerations, puncture wounds, tissue avulsions, and crush injuries. The powerful jaws of large dogs, in particular, can cause significant damage. Young children are often bitten on the head or neck, while older children and adults are more likely to be bitten on the limbs.
- Cat bites: Cats have long, sharp teeth, which can cause deep puncture wounds. Bacteria from these wounds can infect tissues beneath the periosteum or within joints, potentially leading to osteomyelitis or septic arthritis, so they should not be taken lightly.
- Human bites: These can be categorized as follows:
- Bites among children may occur during play and often do not break the skin, usually being minor. However, bite marks should be examined—if the intercanine distance (measured from the outer edges of the upper canine teeth) exceeds 2.5 cm, it is likely an adult bite. Children may also bite themselves while nail-biting or thumb-sucking, which may require medical evaluation to rule out other conditions. Occasionally, parents trimming an infant's nails by biting rather than cutting them can lead to paronychia.
- Skin broken by teeth often occurs when a clenched fist strikes another person's teeth. A break in the skin over the knuckles can introduce both skin and oral bacteria into the hand's fascial layers, potentially spreading to nearby joints. This may result in deep soft tissue infections, septic arthritis, or osteomyelitis.
- Bites to the breasts or genitals may occur during sexual activity or assault.
How should the severity of wounds from animal bites be classified?
Rabies exposure refers to being bitten, scratched, or licked on mucous membranes or broken skin by a rabid, suspected rabid, or undetermined rabid animal (primarily dogs), or direct contact of open wounds or mucous membranes with saliva or tissues potentially containing the rabies virus. Rabies exposure is classified into three levels based on the nature and severity of the exposure:
- Level I: Touching or feeding animals, with intact skin being licked, or intact skin coming into contact with secretions or excretions from a rabid animal or human rabies case.
- Level II: Minor bites on exposed skin without bleeding, or minor scratches or abrasions without bleeding.
- Level III: Single or multiple penetrating bites or scratches (visible bleeding or subcutaneous tissue exposure); broken skin being licked; mucous membranes contaminated by animal saliva; or exposure to bats. Bites on the head, face, neck, or external genitalia are classified as Level III exposure.
What clinical manifestations or complications may occur if an infection develops after an animal or human bite?
- Clinical signs of a bite wound infection may include fever, redness, swelling, tenderness, pus discharge, and lymphangitis.
- Complications may include subcutaneous abscesses, osteomyelitis, septic arthritis, tenosynovitis, and bacteremia.
What are the risks of being scratched by a cat?
The main risks of cat scratches include:
- Wound infection.
- Cat-scratch disease: This is the most common disease caused by cats, resulting from infection with a virus carried by cats. About 40% of cats carry this pathogen at some point in their lives without showing symptoms. If untreated, cat-scratch disease can severely damage organs such as the eyes, brain, liver, or spleen.
- Tinea corporis: The affected skin may develop raised, scaly patches.
- Toxoplasmosis: Toxoplasma gondii, a parasite found in cats, can be transmitted through cat feces. If a person is scratched by a cat, especially if the claws are contaminated with feces, they may become infected with Toxoplasma gondii, which poses significant risks, particularly for pregnant women.
CAUSES
In What Situations Are Dog Bites More Likely to Occur?
Do not approach dogs in the following states, as they may dislike being disturbed. If someone gets close to them or bothers them, they might mistakenly think people are trying to take their food or harm them, which could trigger aggressive behavior:
- Dogs that are eating;
- Dogs playing with toys;
- Dogs that are sleeping;
- Mother dogs with puppies;
- Dogs left alone in cars;
- Dogs confined in cages, pens, or tied up;
- Stray dogs without owners.
DIAGNOSIS
What tests are needed after animal and human bites?
- If the bite wound is infected and shows signs of systemic infection, aerobic and anaerobic blood cultures should be obtained before starting antibiotic therapy to facilitate targeted treatment.
- Patients with deep dog bites to the scalp, including puncture wounds, require a head CT, especially children under 2 years old.
- Deep bites near joints require plain X-rays to assess bone or joint damage and the presence of foreign bodies such as embedded teeth.
- Ultrasound may help identify abscess formation in infected wounds and locate certain foreign objects.
TREATMENT
Animal and Human Bites: When Should You Seek Medical Attention?
- Seek immediate medical attention if any of the following apply:
- Bitten or scratched by a dog or cat suspected or confirmed to have rabies. If the vaccination status of the animal is unknown, seek medical care.
- Bitten by a wild animal (e.g., bat) that may carry rabies.
- Bitten by a cat (cat bites often cause infections) or human, with broken skin.
- Deep or large wounds from dog or human bites, or if joint movement is restricted.
- Any animal bite if you have diabetes, liver disease, cancer, HIV/AIDS, or take immunosuppressive drugs.
- Bleeding persists after 15 minutes of direct pressure.
- Last tetanus shot was over 5 years ago, or vaccination history is unknown.
- Worsening pain, redness, warmth, fever, or pus discharge from the wound.
Animal and Human Bites: Emergency First Aid
- Thoroughly wash the wound with soap and water for several minutes, even if it stings, to prevent infection.
- For bleeding, apply pressure with a clean cloth or bandage, then seek medical care immediately.
- For Category II and III exposures, proper wound care is critical to prevent rabies and bacterial infections.
Animal and Human Bites: Medical Treatment
Doctors will clean and disinfect the wound. Suturing may be needed depending on size and location. Antibiotics, tetanus shots, or hepatitis B vaccines may be administered based on the case.
Animal and Human Bites: Is Immediate Vaccination Always Necessary?
It depends:
- If your pet (dog/cat) has been vaccinated for rabies for two consecutive years and the bite occurred during normal play, observe the animal for 10 days (WHO’s 10-day observation rule). Rabies transmission only occurs if the animal shows symptoms.
- If the animal shows abnormalities during observation, get vaccinated immediately.
- For stray animals or unobservable cases, immediate rabies vaccination is required. Doctors may also recommend rabies immunoglobulin.
- Human bites generally don’t require rabies vaccination unless the biter is infected.
Animal and Human Bites: Follow-up Care
Patients should return for wound evaluation within 48–72 hours as advised.
What Is Rabies?
Rabies is a viral disease transmitted through bites from infected animals. Unvaccinated dogs and cats are common carriers. No cure exists, but prompt wound care and post-exposure prophylaxis can prevent onset.
Animal Bites: Do You Need Rabies Vaccination?
Exposure is categorized into three levels:
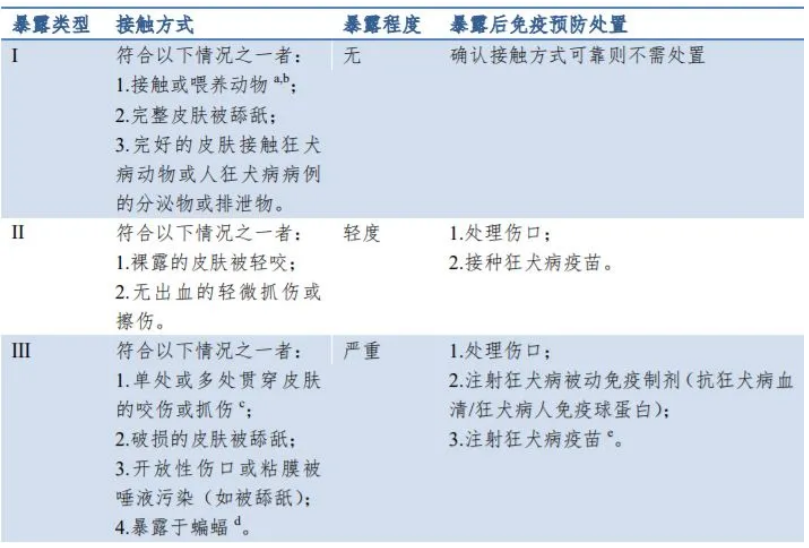
- Category I: No vaccination needed.
- Categories II & III:
- 5-dose regimen: Days 0, 3, 7, 14, and 28.
- 2-1-1 regimen: 2 doses on Day 0 (one in each arm), then 1 dose on Days 7 and 21 (approved vaccines only).
Note: Category III cases, immunocompromised individuals, or facial exposures require rabies immunoglobulin alongside vaccination, ideally administered immediately after wound cleaning (within 7 days of first vaccine dose).
DIET & LIFESTYLE
None.
PREVENTION
How to Avoid Being Bitten by an Unfamiliar Dog?
- When encountering an unfamiliar dog, do not run or make sudden movements;
- Do not shout, scare, or tease the dog;
- Avoid staring directly into the dog's eyes;
- Do not kick, hit, or pull the dog.